The comprehensive user manual for Siemens SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES vector control series covers seven core modules: system overview, configuration connections, EMC design, functional parameters, parameterization steps, communication interfaces, and safety functions. It supports multiple control modes such as V/f control, encoder free vector control, and encoder vector control, and is compatible with a power range of 0.55kW-2300kW. It has multiple communication protocols such as PROFINET/PROFIBUS, STO/SS1 safety functions, and flexible parameterization methods. It can be configured through PMU/OP1S/DriveMonitor and is suitable for high-precision drive control in multiple scenarios of industrial automation.
Overview of System Core
1. Basic product information
Notes on Core Parameters of the Project
Product series SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES Vector Control (VC) including Motion Control (MC) derivative models
Power range 0.55kW-2300kW Compact PLUS type 0.55-18.5kW, chassis type 45-2300kW
Control mode V/f control, vector control without encoder, vector control with encoder, torque control adapted for asynchronous/synchronous motors
Modular design of core components such as rectifier, inverter, CUVC control board, braking unit, and communication board (CBP/CBC), supporting multi axis expansion
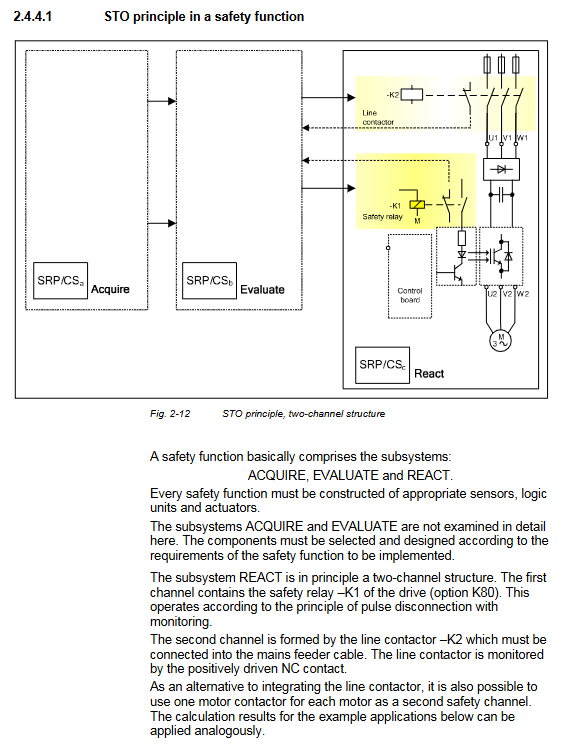
Security level SIL2/SIL3, PL d/e, Cat.3/4 support STO/SS1 security function
Communication interface USS, PROFINET DP, PROFIBUS DP, SIMULINK, CAN optional communication board expansion
2. Core advantages
Multi mode adaptation: supports multiple modes such as V/f and vector control to meet different accuracy requirements
Security integration: Built in STO/SS1 security function, compliant with EN 61800-5-2 standard
Flexible expansion: Single axis/multi axis configuration is optional, supporting up to 3-axis collaborative drive
Precise control: With encoder vector control mode, it has fast dynamic response and high torque accuracy
Convenient debugging: supports PMU/OP1S/DriveMonitor three parameterization methods
Hardware configuration and connection
1. Equipment type and specifications
Equipment type, power range, installation method, core characteristics
Compact PLUS 0.55-18.5kW DIN rail installation integrated design, suitable for single axis/multi axis drive
Compact 2.2-37kW panel mounted independent power unit, supporting expansion
Chassis type 45-2300kW cabinet installation for high-power scenarios, supporting water cooling options
Water cooled on-demand matching cabinet installation suitable for high temperature environment, stable operation
2. Typical configuration scheme
Single axis drive: 1 rectifier+1 inverter, suitable for independent drive scenarios
Multi axis drive (≤ 3 axes): 1 rectifier+multiple inverters, sharing DC bus
Multi axis drive (>3-axis): common rectifier unit+multiple inverters, external 24V power supply
Safety configuration: Safety relay+STO/SS1 circuit, dual channel structure ensures safety
3. Wiring specifications
Power wiring: 3-phase AC 380-480V input, DC bus 510-650V, wire specifications 0.75-120mm ²
Signal wiring: Analog quantity (-10~+10V/0~20mA), digital quantity (24V DC), encoder signal (HTL/TTL)
Shielding requirements: Motor cables/signal cables need to be shielded, with both ends of the shielding layer grounded, and a minimum bending radius of 10 times the cable diameter
Safe wiring: The STO function requires dual channel wiring, and the emergency stop button is connected in series with the safety circuit
Detailed explanation of core functions
1. Control function
Functional Type Core Parameters Applicable Scenarios
V/f control voltage frequency curve, slip compensation, boost function fan, pump universal load
Without encoder vector control, the speed accuracy is ± 0.5%, the torque response is fast, and there is no need for high-precision speed measurement scenarios
Vector control speed accuracy with encoder ± 0.01%, 1024 line high-precision drive with pulse encoder (machine tool, conveyor belt)
Torque control with torque accuracy of ± 5%, adjustable torque limit and tension control (winding equipment)
2. Safety features
Standard basis for safety function description
STO (Safe Torque Off) cuts off the motor torque output to prevent accidental starting EN 61800-5-2, Stop Category 0
SS1 (Safe Stop 1) time controlled deceleration cuts off torque, controllable shutdown EN 61800-5-2, Stop Category 1
Dual channel design for safety circuit, diagnostic coverage rate of 90%+EN ISO 13849-1:2008
3. Auxiliary functions
Automatic motor recognition (P115): supports static/dynamic recognition, automatically matches motor parameters
Fly start (P130): Smooth start when the motor rotates to avoid surge current
Kinetic Energy Buffer (KIB): Utilizing the kinetic energy of the motor to maintain the DC bus voltage during power outages
DC braking: quick stop, adjustable braking time (0-100s)
Temperature adaptive: Adjust the output according to the motor temperature to protect the motor
Parameterized operation
1. Comparison of parameterization methods
Parameterized tool operation method, core advantages, applicable scenarios
PMU (panel) local button operation, 4-digit 7-segment display without additional equipment, quick setup, simple debugging, troubleshooting
OP1S (operation panel) displays in Chinese/English, supports parameter upload and download, has strong portability, and supports multi slave site and multi device debugging
DriveMonitor (software) PC operation, graphical interface for batch configuration, script editing for complex system configuration, offline debugging
2. Key parameterization process
Factory reset: P053=6 → P060=2 → P970=0, restore default parameters
Quick parameterization (P060=3): Input motor nameplate data → Select control mode → Set command source → Automatic parameterization
Detailed parameterization: power segment definition → board configuration → motor parameters → control parameters → communication parameters → safety parameters
Parameter backup: OP1S or DriveMonitor upload parameter set, supports batch download
3. Core parameter group
Function description of key parameters in parameter group
Motor parameters P101 (rated voltage), P102 (rated current), P107 (rated frequency), P108 (rated speed) match the motor nameplate data
Control parameters P100 (control mode), P235 (speed loop gain), P240 (speed loop integration time) to adjust and control dynamic performance
Instruction parameters P443 (main given source), P554 (ON/OFF 1 source), P573 (MOP rise) define the control instruction source
Configure safety loop signals for safety parameters P651 (digital output source) and P698 (SCI digital output)
Communication interface
1. Detailed explanation of communication protocol
Protocol type, transmission rate, number of connections, core usage
USS 9.6-19.2kBd up to 32 slave stations with simple bus control and parameterization
PROFIBUS DP 9.6kBd-12MBd up to 126 slave industrial automation network integration
PROFINET IO 100MBd real-time communication high-precision synchronous control
SIMOLINK 100MBd with up to 200 nodes for multi axis synchronization and high-speed data transmission
CAN 1Mbps up to 31 nodes low-cost distributed control
2. Key points of communication configuration
Address setting: USS/PROFIBUS addresses 1-247 to avoid conflicts
Baud rate matching: All slave stations must have the same baud rate as the master station
Bus terminal: Terminal resistors (120 Ω) need to be connected at both ends of the PROFIBUS/CAN bus
Protocol selection: Choose based on real-time requirements, prioritize high-precision synchronization PROFINET/SIMOLINK
EMC Design Specification
1. Core EMC rules
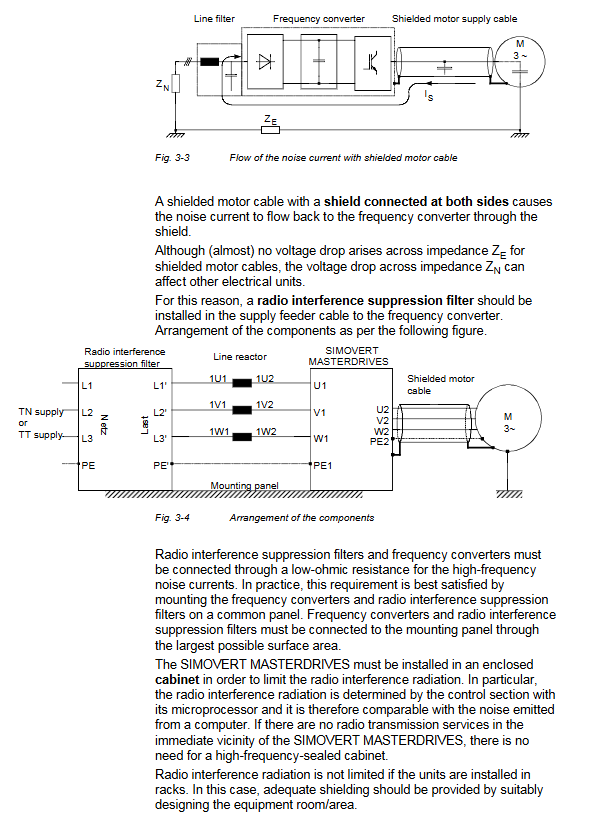
Partition isolation: Install noise sources (inverters, braking units) and sensitive equipment (controllers, sensors) in different zones
Cable separation: The distance between power cables and signal cables should be ≥ 20cm, and cross wiring should be done vertically
Shielding treatment: The shielding layer of the motor cable/signal cable is grounded 360 ° without interruption
Grounding requirements: The grounding resistance of the cabinet should be ≤ 4 Ω, and all metal components should be reliably grounded
Filter configuration: Install EMC filter on the power side to reduce harmonic interference
2. Typical EMC configuration
Input side: EMC filter+incoming reactor to suppress conducted interference
Output side: dv/dt filter/sine filter, reducing motor cable radiation interference
Signal side: Use shielded twisted pair cables for analog signals, away from power cables
Safety and Compliance
1. Safety operation requirements
Qualification requirements: Only qualified personnel are allowed to operate, and familiarity with the safety manual is required
Power off operation: Before wiring/maintenance, disconnect all power sources and wait for the capacitor to discharge
Electromagnetic radiation: The device generates an electromagnetic field during operation, and pacemaker wearers should stay away from it
Environmental restrictions: It needs to be installed in a closed cabinet to avoid contact with high-temperature components
2. Compliance standards
International standards: IEC 61800-5-2 (safety), IEC 60947 (electrical safety) EN 55011(EMC)
Domestic standard: GB/T 12668 (Variable Speed Electrical Transmission System)
Certification qualifications: CE, UL, CSA, CCC


Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *