MOVIDRIVE ® The complete process of technology application frequency converter debugging through PROFIBUS DP-V1 fieldbus revolves around CFP21A fieldbus card (supporting addresses 1-125) MOVISUITE ® Engineering design software and TIA Portal programming tools are developed, covering PROFIBUS network configuration, frequency converter address setting, process data configuration MOVIKIT ® The key operations such as software module application (Velocity Drive/Positioning Drive) and equipment replacement emphasize EMC compliant wiring, diagnostic alarm function, and safety debugging specifications, which are suitable for industrial automation integration scenarios with PLCs such as SIMATIC S7.
1、 Basic information of the document
Project Details
Applicable equipment MOVIDRIVE ® Technology application frequency converter (MDX9 series)
Core bus PROFIBUS DP-V1 (supports periodic/non periodic communication)
Key hardware includes CFP21A fieldbus card, USM21A interface adapter, CBG21A handheld controller
Support software MOVISUITE ® (Engineering Design), TIA Portal (PLC Configuration) MOVIKIT ® software module
Compliance standards PROFIBUS PI specification, IEC 61158 (bus cables), EMC wiring requirements
2、 PROFIBUS network basic configuration
(1) Hardware and wiring requirements
Bus cable: shielded twisted pair (IEC 61158 type A), with a large area of grounding at both ends of the shielding layer
Bus terminal: PROFIBUS segment head and tail devices enable terminal resistors (integrated into the plug)
Address setting: Set through the DIP switch of CFP21A (1-125), default address is 4, and it needs to be restarted to take effect after modification
Wiring specifications: laid in separate trenches with power cables, with a spacing of ≥ 20cm; metal cable racks for industrial environments
(2) Equipment Description Document (GSD)
File Name: SEW_6011.gsd (Non modifiable)
Download path: SEW official website → Online Support → Data and Files → Software → Search for “GSD Files”
Function: Provide all the parameters required for frequency converter engineering design and data exchange, which is a prerequisite for PLC configuration
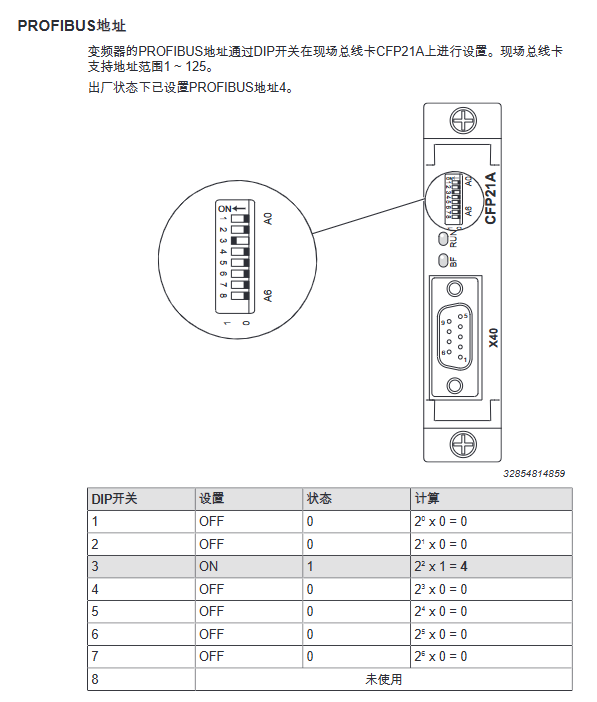
3、 Core debugging process
(1) Preliminary preparation
Hardware connection: Engineering design computer → USM21A → Inverter X32 interface (9-pin D-type)
Address setting: Use the DIP switch of CFP21A to set the PROFIBUS address (1-125)
Software preparation: Install MOVISUITE ®、 TIA Portal, Download the latest GSD file
(2) PLC side configuration (TIA Portal)
Key instructions for steps and operation content
- Create a new project and install the GSD file to import SEW_6011.gsd, ensuring version matching
- Add PLC and set PROFIBUS interface to select SIMATIC S7, configure IP address
- Add frequency converter device path: Other on-site devices → PROFIBUS DP → SEW-EURODRIVE → MOVI-C MOVIDRIVE
- Allocate PROFIBUS address consistent with CFP21A set address
Add 5 configuration process data words from slot 2 onwards (5 words/8 words, up to 16 words)
Download the project to PLC, save the project, and establish the communication link
(3) Inverter side configuration (MOVISUITE) ®)
Network scanning: Select USB network type, scan and apply frequency converter devices
Device configuration: Assign device name, download MOVIKIT ® Software modules (recommended) or manually configuring process data sources
Parameter settings: Configure the mapping between set values and actual values, save the project and download it to the frequency converter
(4) Process data validation
Method 1: MOVIKIT ® Diagnostic Monitor
Monitoring mode: Observe the process data transmission between PLC and frequency converter (control word/status word/speed, etc.)
Control mode: Disable fieldbus data and set parameters directly through software (dangerous area needs to be locked)
Method 2: MOVISUITE ® Process data buffer
Check the consistency between PO data (PLC set value) and PI data (actual value of frequency converter)
4、 Key functional modules
(1)MOVIKIT ® software module
Module Type Core Function Process Data Word Quantity Applicable Scenarios
Velocity Drive speed regulation drive, torque control 5-word ordinary speed regulation scenario
Positioning Drive 8-character high-precision positioning scene (machine tool/robot)
(2) Parameter access function module
Module Name: SEW-MOVI-CSingleParameterAccess (FB200)
Function: Read and write frequency converter parameters through non periodic communication via PROFIBUS
Supporting Protocol: Simple MOVILINK ® Protocol(SMLP)
Example project: TIA Portal example can be downloaded from the SEW official website
5、 Fault diagnosis and equipment replacement
(1) LED indicator diagnosis
Measures for handling the meaning of LED name status
BF (red) long on communication interruption/unrecognized baud rate check cable/PLC configuration
BF (red 2Hz flashing) not addressed by PLC/configuration error check address/GSD file
RUN (green) constantly on, bus hardware is normal, no
RUN (red 2Hz flashing) Address 0 or>125 Reset address and restart
(2) Diagnostic Alert
Enabling method: TIA Portal device view → Slot 0 → General DP parameters → Enable diagnostic alerts
Function: Report fault number/description in text form to PLC component diagnosis
Default state: Factory enabled
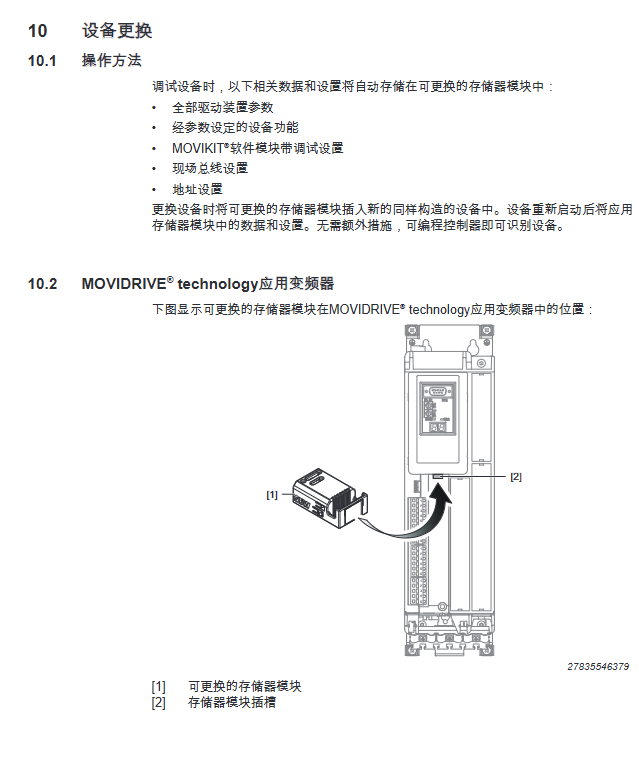
(3) Equipment replacement
Operation: Insert the memory module of the old device into the new device (of the same model)
Inheriting data: driver parameters MOVIKIT ® Configuration, fieldbus settings, address information
Advantage: No need for reconfiguration, PLC automatically recognizes new equipment
6、 Safety regulations
Network security: Restrict Ethernet/engineering interface access and comply with IT security standards
Debugging safety: Lock the hazardous area in control mode and activate existing safety devices
Wiring safety: Power cables and signal cables are laid in separate trenches, and the shielding layer is reliably grounded
Operation permission: Only trained professionals are allowed to perform software operations


Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *