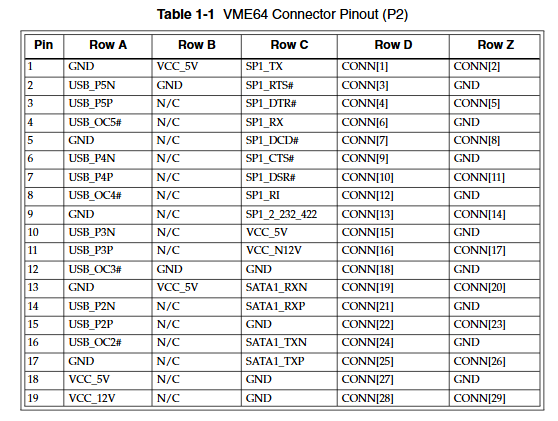
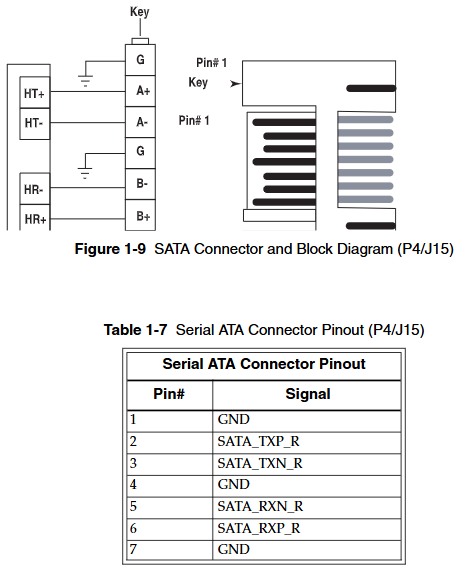
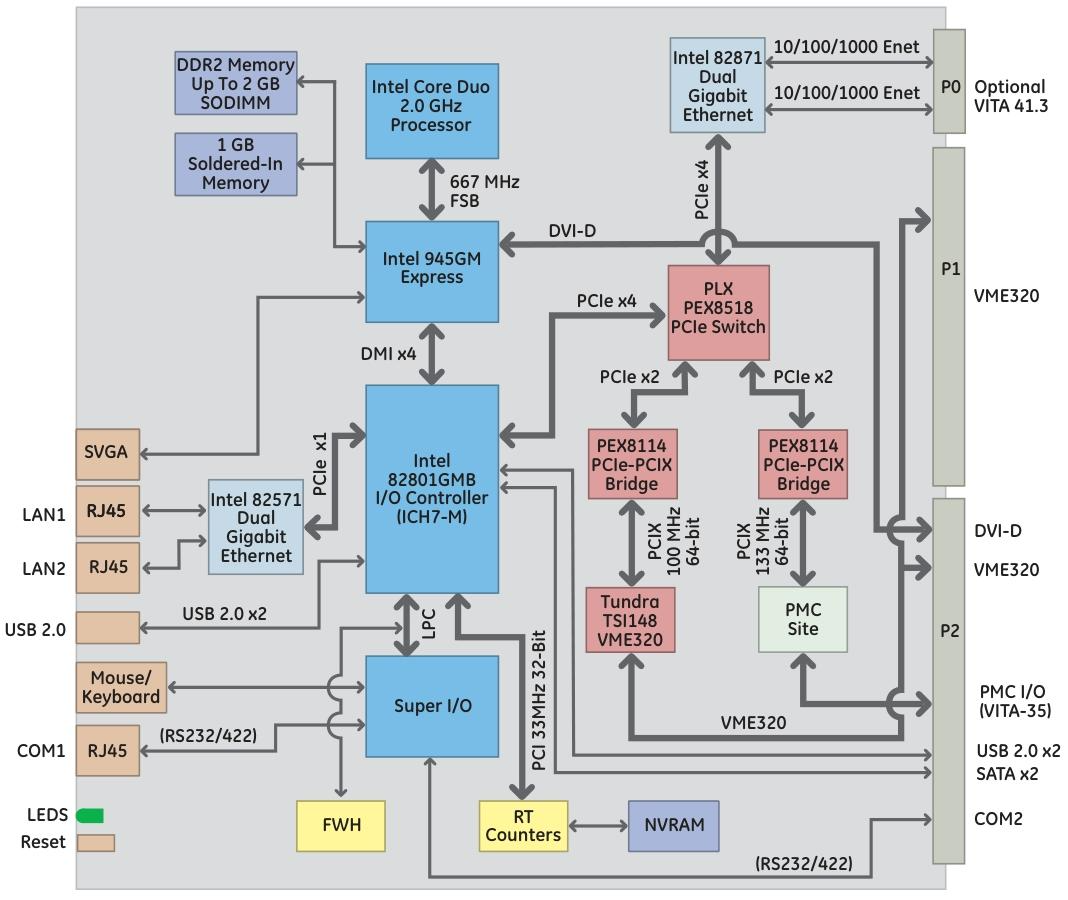
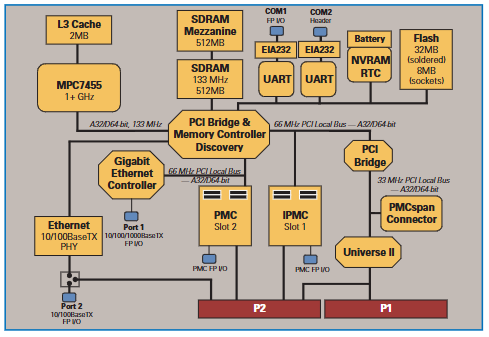
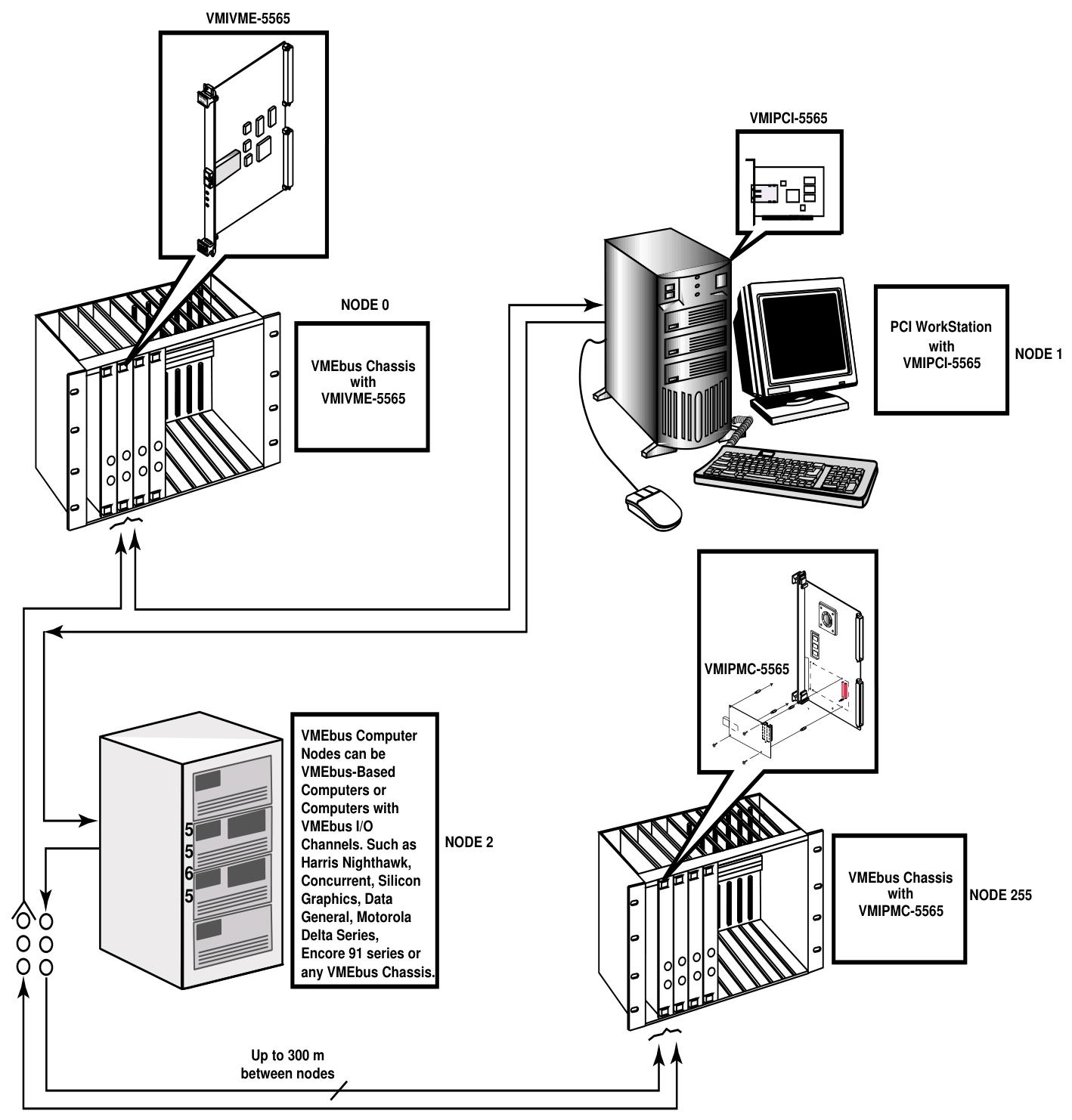
GE VMIVME-1182 64 channel isolated digital input board
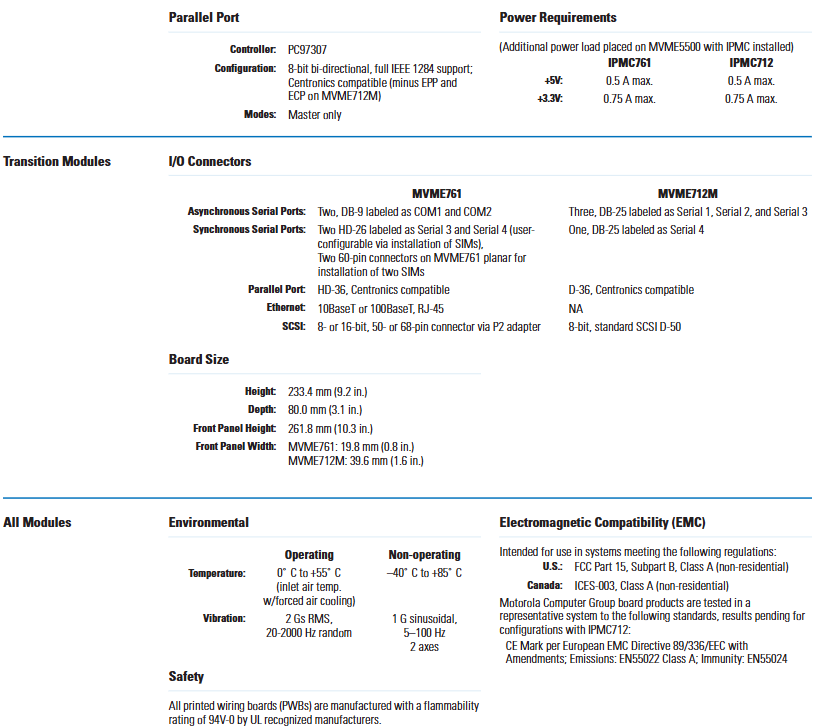
Basic characteristics
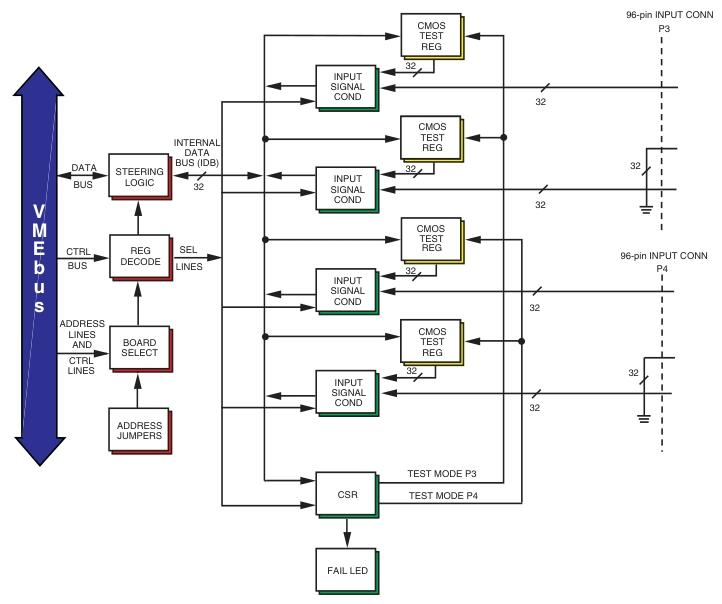
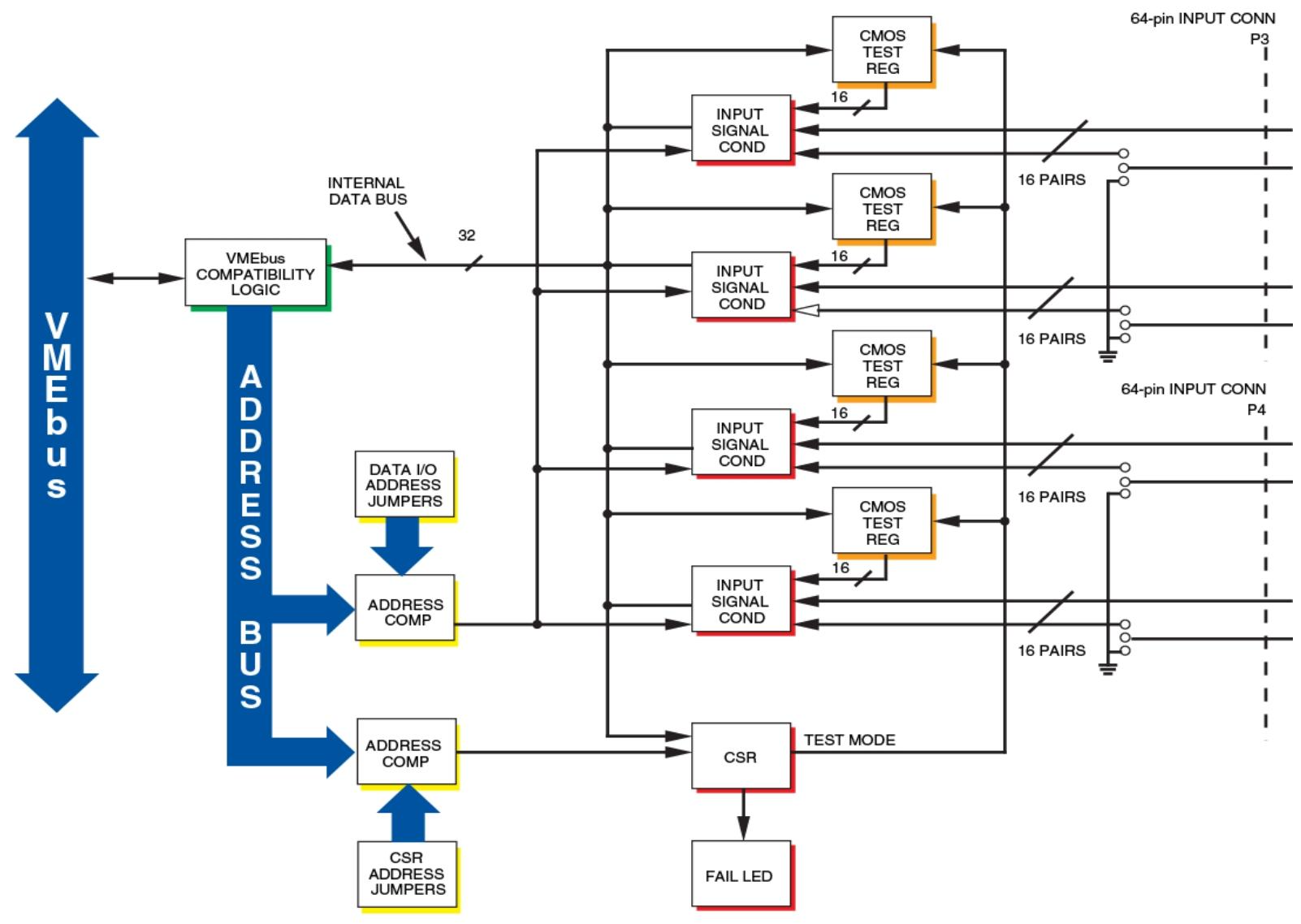
It has 64 optically isolated input channels and supports multifunctional operations for each channel, including monitoring of state changes (COS), sequence of events (SOEs), pulse accumulation, programmable debounce time, and time stamps.
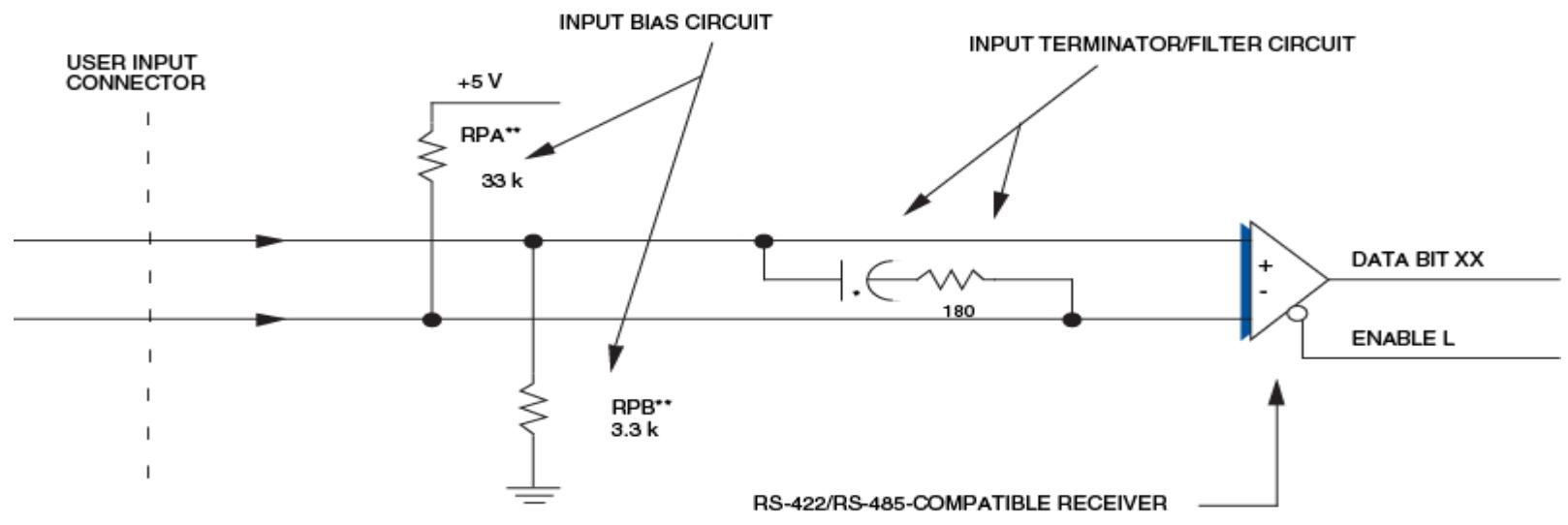
The input voltage range covers 5-250VDC or 4-240VAC, and the isolation between channels and between channels and VME bus can reach 1500VDC or 1100VRMS.
The pulse accumulation range is 0-65535 pulses, supporting channel by channel monitoring of SOEs. The debounce time and COS function can be controlled channel by channel through software.
The measurement interval is 1.0ms, and COS can be disabled, rising edge (low to high transition), falling edge (high to low transition), or triggered by any edge.
Supports short/standard, monitoring, non privileged, or arbitrary access modes, with user selectable interrupt levels, compatible with UIOC ®。
When used in conjunction with a matching suppression panel (such as VMIVME-3459), it complies with the ANSI/IEEE STD C37.90.1-1989 surge protection standard.
Application area
Data acquisition system, nuclear power plant monitoring, control system, etc.
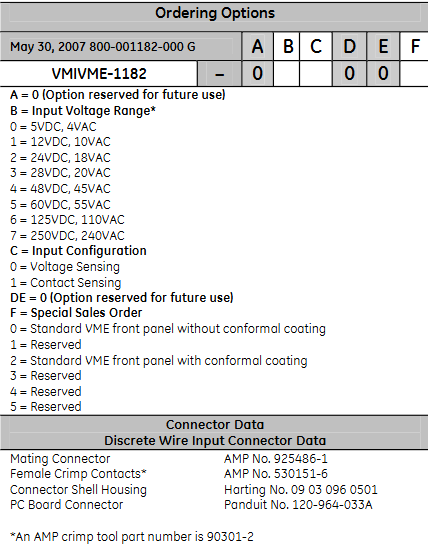
ordering information
The meaning of each parameter in the ordering options: A is a reserved option (0); B represents the input voltage range (0-7 corresponds to different AC and DC voltages); C is the input configuration (0 is voltage sensing, 1 is contact sensing); DE is a reserved option (0); F is a special sales order (0-5 corresponds to different panel configurations).
Discrete line input connector related information: The matching connector is AMP No.925486-1, the female contact point is AMP No.530151-6, the connector housing is Harting No.09 03 096 0501, the printed circuit board connector is Panduit No.120-964-033A, the AMP crimping tool model is 90301-2, and DC or AC can be selected through software.
Functional feature details
Basic functions: It can detect COS with 64 digital inputs, perform time tagging and counting. The onboard buffer can store COS information with time tags to analyze SOEs. The pulse accumulator is used to count COS. When COS is detected, it can be programmed to issue an interrupt, and each channel processes it independently.
COS timing: The input signal is latched every millisecond, and after a programmable debounce time (1.25ms-1.024s), if a valid COS is detected, it will be time marked and stored by a millisecond timer. The minimum reliable detection pulse time is 2ms.
COS detection: Programmable detection of rising edge, falling edge, or both, detecting COS can generate interrupts or disable.
Time stamping: Each COS event can be marked with a timer value of 0-65s, which updates every millisecond. When the maximum value is reached, it resets to zero and notifies the host.
Sequence of Events (SOE): SOE memory is allocated to two buffers (each capable of storing 3000 events), where the host processes one buffer while the other can load new event data. SOE logic can issue interrupts to the host at the end of the buffer or when the user sets a count.
Pulse Accumulation: Each channel has a Pulse Accumulation Count (PAC) register, and when the count reaches 65535, it will notify the user through a flag in the control register or issue an interrupt.
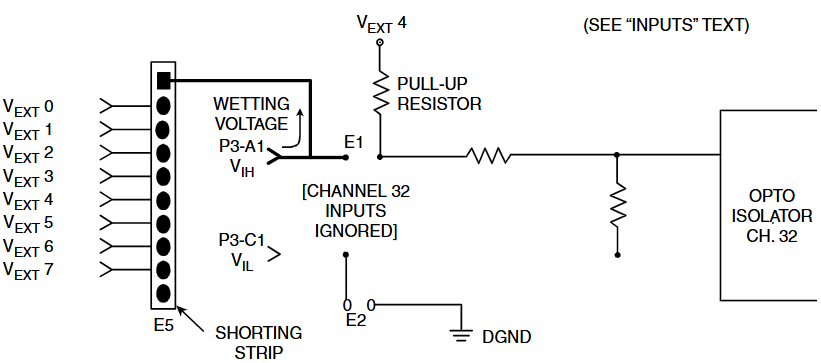
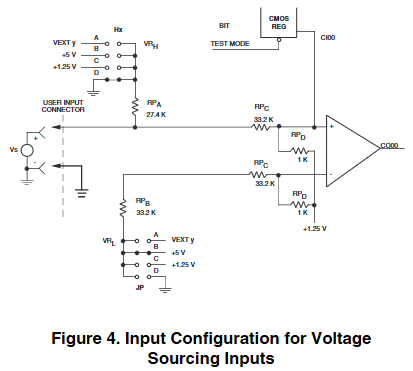
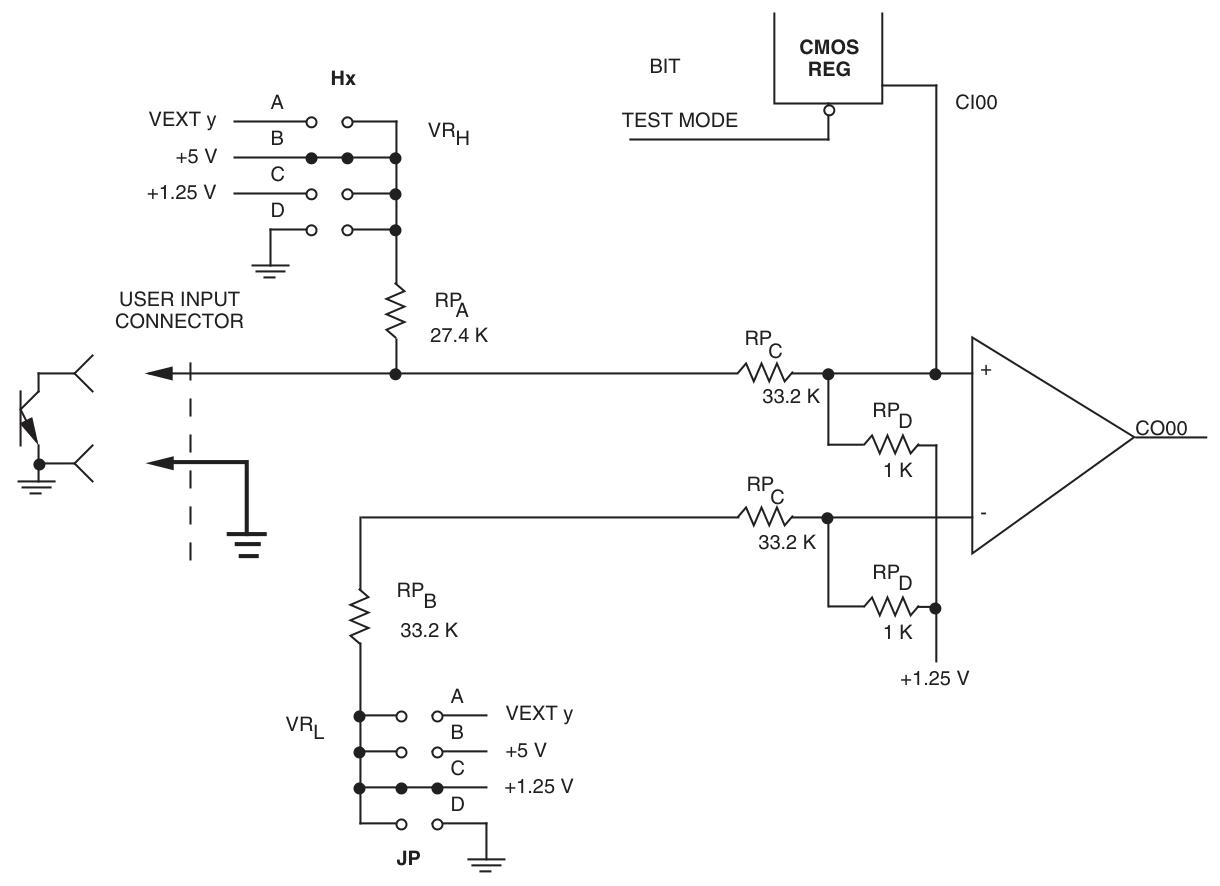
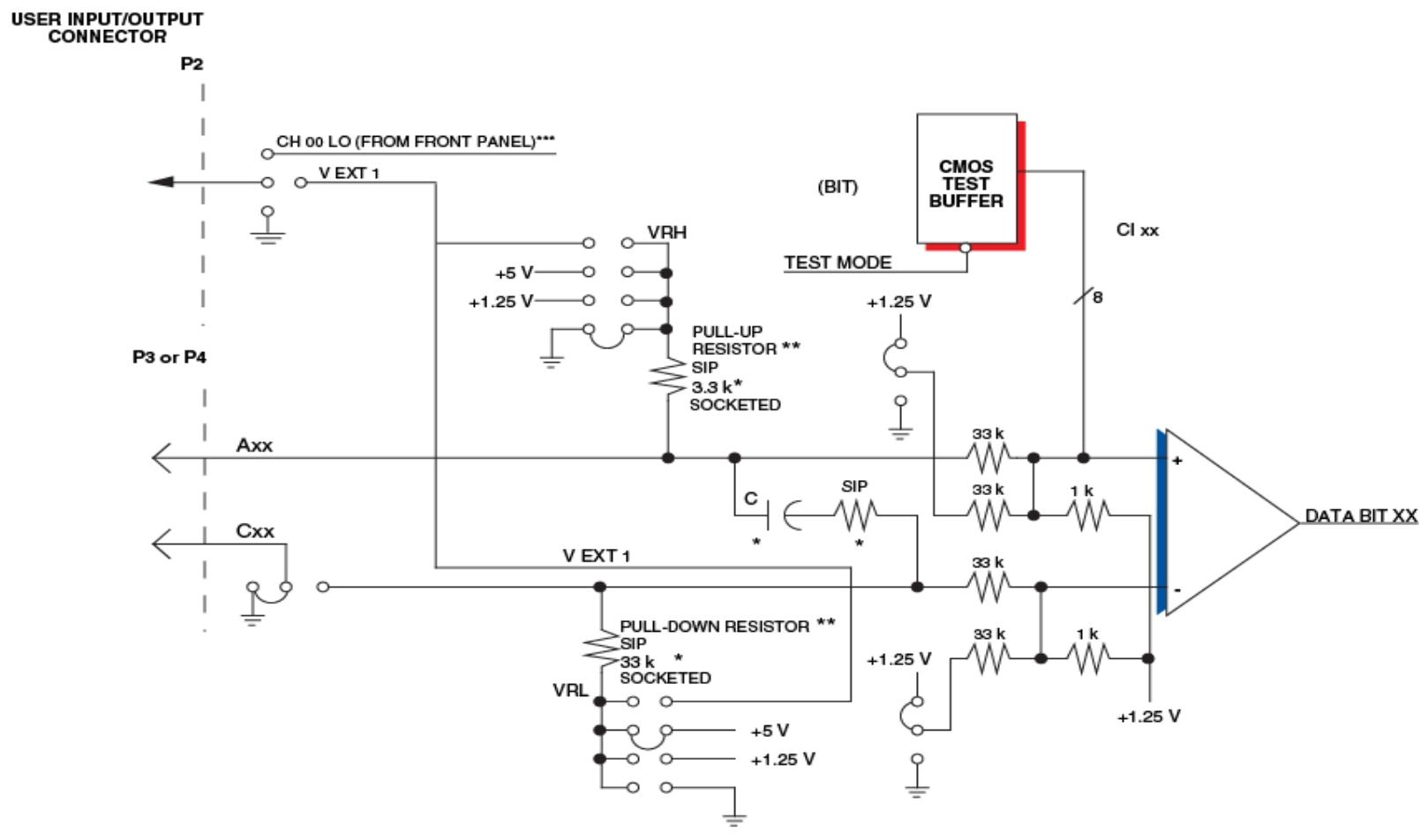
Input configuration: divided into voltage sensing and contact sensing options. The contact sensing option is equipped with a pull-up resistor to the wetting voltage pin, while the voltage source option has no pullups and has 8 wetting voltage input pins. Channel 32 can be changed to a wetting voltage supply through jumper wires.
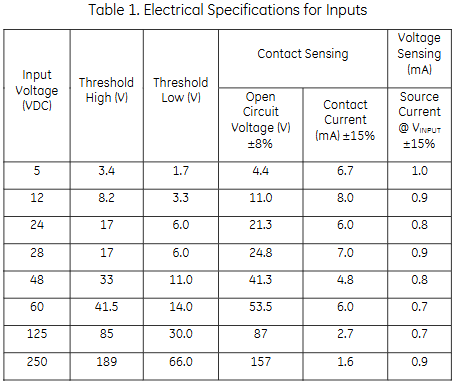
Electrical specifications
Provides high threshold, low threshold, contact induction (open circuit voltage, contact current), and voltage induction (source current) parameters corresponding to different input voltages (VDC), with a minimum inter channel crosstalk suppression of 80dB (1kHz) and a minimum common mode suppression of 80dB (DC-60Hz).
VME compliance
Compliant with the VMEbus specification (ANSI/IEEE STD 1014-1987, IEC 821 and 297), it provides response address modifiers, data access modes, and interrupt situations corresponding to different addressing modes.
Other characteristics
Board address: Set the basic VME address through jumper wires, with an address space of 8K words.
VME access: Address modifier bits are selected and decoded through jumpers, supporting non privileged, monitored, and both board access.
Self check: The system automatically runs after resetting, or it can be run by activating the test mode bit in CSR. The self check result is stored in the control register space, and the LED status does not change with the self check result. It mainly checks the integrity of the microcontroller and onboard memory.
System reset: After reset, there are default conditions such as input transmission (1ms debounce), LED lighting, and test mode activation.
Front panel status LED: It lights up after system reset and can be controlled by software switch.
Interrupt: It can be issued at any level, and after confirmation, the bus will place a single byte vector. There are multiple interrupt triggering conditions that can be enabled/disabled.
Physical/Environmental Specifications
Dimensions: Height 9.2 inches (233.4mm), Depth 6.3 inches (160mm), Thickness 0.8 inches (20.3mm).
Power requirement: Typical value of 2.0A at 5V, plus power consumption of pull-up resistor.
Cooling method: forced air cooling.
Temperature range: working 0-65 ° C, storage -25-85 ° C.
Altitude: Working at 0-10000 feet (3048m).
Humidity: Operating relative humidity of 20% -80%, non condensing.
Maximum weight: 0.7kg.