YOKOGAWA FCN/FCJ Autonomous Controller
Product Overview
(1) Product positioning and core applications
FCN/FCJ are two core autonomous controllers under Yokogawa Electric Corporation’s STARDOM series, designed specifically for industrial automation scenarios. They are suitable for various industrial processes from sequence control to analog control, and can achieve core functions such as equipment linkage, parameter adjustment, data acquisition, and monitoring. The two products are designed with modularity (FCN) and integration (FCJ) respectively, adapting to different installation environments and system complexity requirements. They are widely used in distributed control systems in factories, built-in control of mechanical equipment, industrial process monitoring and other scenarios, providing highly reliable and efficient control solutions for industrial production.
(2) Product Classification and Definition
Product type, English abbreviation, meaning, structural characteristics, subdivision models, and core configurations
FCN Field Control Node has a modular structure that can be flexibly matched with CPU, I/O, and other expansion modules according to needs, with strong scalability – FCN-100: equipped with NFCP100 CPU module
-FCN-500: Equipped with NFCP501/NFCP502 CPU modules
-FCN-RTU: equipped with NFCP050 CPU module, low-power design
FCJ Field Control Junction integrated structure, built-in I/O interface, no need for additional module assembly, compact structure without subdivision models, unified as FCJ series, integrated control and I/O functions
Core product features
(1) High performance: adaptable to diverse control requirements
Multi process compatibility: It can seamlessly integrate various industrial processes such as sequence control and analog control, and can meet the control needs of different processes without the need to replace controllers, reducing system upgrade and maintenance costs.
Flexible operation mode: supports independent operation (single controller completes local control) and interconnected control (communicates and links with other autonomous controllers or external devices), adapting to system architectures ranging from simple to complex.
Software linkage extension:
Paired with Versatile Data Server (VDS) or Supervisory Systems (FAST/TOOLS), a feature rich operation and monitoring system can be built to achieve advanced functions such as centralized data management, visual monitoring, and report generation.
Supports FCN/FCJ OPC servers, and PC OPC clients (following the OLE for Process Control standard) can directly access controller data, achieving cross platform data interaction.
Java Scalability: Built in Java Virtual Machine, supporting various Java application development and deployment, including:
Web browser image display: Visualize device status, control parameters, and other information through web pages.
Data management: Save data files locally and transfer files through FTP protocol.
Communication extension: Sending/receiving emails (supporting SMTP/POP3 protocol and SMTP server authentication), connecting to the public network through PPP protocol (such as GPRS network).
Programming free application: Paired with InfoWell software, web browsing, email communication, and other functions can be achieved without writing code, reducing the threshold for application deployment.
(2) High reliability: ensuring continuous operation of industry
Comprehensive diagnosis and protection: Equipped with complete RAS features (CPU self diagnosis, temperature monitoring, I/O diagnosis, etc.), it can monitor the equipment’s operating status in real time, detect faults in a timely manner, and issue alarms; Equipped with ECC (Error Correcting Code) error correction memory, effectively avoiding control exceptions caused by memory data errors.
Low power fanless design: High heat dissipation efficiency, stable operation without the need for a cooling fan, reducing mechanical failure points, suitable for harsh environments with high dust and vibration in industrial sites.
Dual redundant configuration:
FCN-100: The Ethernet control network, CPU module, power module, and SB bus (local bus) can all be configured with dual redundancy, allowing seamless switching in case of any component failure without downtime.
FCJ: The control network supports dual redundancy to ensure the continuity of communication links and meet the high reliability communication requirements of distributed systems.
(3) Engineering Efficiency: Simplify Development and Configuration
Multi programming language support: compatible with 5 IEC 61131-3 standard programming languages (such as ladder diagrams, functional block diagrams, instruction lists, etc.), users can flexibly choose according to process requirements and development habits, reducing programming barriers.
Software component reuse: Control logic can be encapsulated as standardized software components, supporting reuse, avoiding duplicate development, improving system configuration efficiency and consistency, and ensuring control quality.
Application Portfolios: Built in Yokogawa Electric’s years of industrial application experience, providing rich pre made software packages that can quickly implement advanced functions, including:
Control class: Control circuit instrument blocks (such as PID controllers, indicators, etc.).
Communication class: Communication adaptation module for non Yokogawa PLCs (such as Mitsubishi MELSEC, Omron SYSMAC, etc.).
(4) Maintainability: Reduce operation and maintenance costs
Online download function: During system operation, control applications can be directly modified, supporting the addition, deletion, and modification of I/O interfaces, variables, data types, program code, and library files. Modifying a single control circuit does not affect the operation of other circuits, and does not require shutdown maintenance, ensuring production continuity.
Hot swappable support: All modules of FCN-100 support hot swappable, so there is no need to cut off the system power when replacing faulty modules, further reducing downtime.
Convenient maintenance tool: supports remote access to the controller through a web browser for network configuration, database backup/recovery, parameter adjustment, and other maintenance operations; Paired with the Resource Configurator tool, hardware parameter configuration can be quickly completed, improving operational efficiency.
System configuration and development maintenance
(1) System configuration type
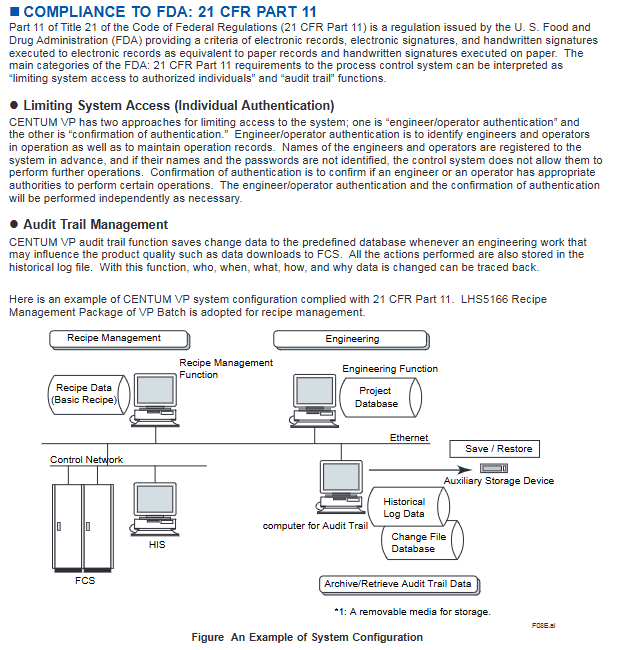
FCN/FCJ are both locally installed controllers that can be flexibly configured with three system architectures according to user on-site needs:
Independent system: A single FCN or FCJ operates independently, suitable for local area control (such as a single device or production unit), with a simple structure and low deployment cost.
Interconnected system: Multiple FCNs/FCJs are interconnected through a control network to achieve cross device linkage control. It supports communication between up to 15 FCNs/FCJs and one controller, adapting to distributed production scenarios such as multi workshop and multi production line collaboration.
Linkage system: One or more FCN/FCJ are linked with upper level software such as VDS, FCN/FCJ OPC Server, FAST/TOOLS, etc., supporting up to four such software to connect simultaneously, achieving centralized monitoring and advanced data management.
Cross device communication: Through the communication module in the application package, it can be interconnected with third-party controllers, display units, temperature controllers, power monitoring devices, and other devices to expand system compatibility.
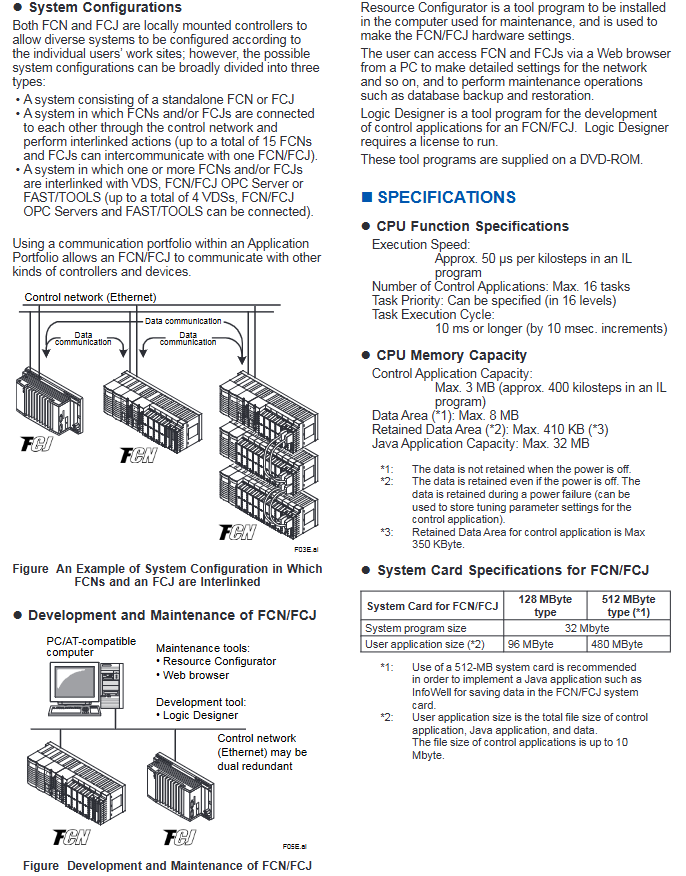
(2) Development and maintenance tools
Tool Name Core Function Operation Requirements
Logic Designer develops FCN/FCJ control applications (organized in task form), supports IEC 61131-3 standard programming language, requires separate license purchase, runs on PC/AT compatible machines
The Resource Configurator is used to configure the hardware parameters of the controller, including IP address, I/O module model, license activation, initial communication protocol settings, etc. No license is required, and it is provided free of charge with the software DVD-ROM
Web browser remote access controller for network configuration, database backup/recovery, device status monitoring and other maintenance operations. Supports mainstream browsers and connects to the controller via Ethernet
FCN/FCJ Simulator simulates the controller operating environment on a general-purpose PC and debugs control applications developed by Logic Designer without the need for actual controller hardware. A separate license needs to be purchased and is provided with the software DVD-ROM
(3) Development and maintenance process
Hardware configuration: Set basic parameters such as controller IP address, I/O module model, communication protocol, etc. through the Resource Configurator tool.
Application development: Use Logic Designer to write control programs (tasks), support multi task parallel design, and specify task priorities and execution cycles.
Debugging and testing: Use FCN/FCJ Simulator to debug the program on the PC side and verify the correctness of the control logic; After debugging, download it to the controller via Ethernet.
Operation and maintenance: During the operation of the system, the device status is monitored through a web browser or local tools. If program modifications are needed, they can be updated through the online download function. In case of faults, modules can be hot plugged and replaced.
Key technical specifications
(1) CPU function and memory specifications
CPU core parameters:
Execution speed: The instruction list (IL) program has a processing speed of about 50 µ s/thousand steps, with high computational efficiency, which can meet the real-time control requirements of industry.
Control application capacity: Supports up to 16 tasks, with task priorities divided into 16 levels and execution cycles ≥ 10 ms (adjusted in increments of 10 ms), suitable for multi task parallel control scenarios.
Memory capacity allocation:
Control application capacity: up to 3 MB, capable of storing approximately 400 thousand steps of IL program.
Data area: Maximum 8 MB, used to store temporary data during runtime, not retained after power failure.
Reserved data area: up to 410 KB (including 350 KB dedicated to control applications), data will not be lost after power failure, and key information such as control parameters and tuning settings can be stored.
Java application capacity: up to 32 MB, used for deploying Java applications.
(2) System card specifications
The system card is used to store system programs, user applications (control programs+Java programs), and data, and offers two specifications to choose from:
System card type, system program occupying space, user application total capacity, recommended usage scenarios
128 MB type 32 MB 96 MB (control application ≤ 10 MB) No complex Java applications, only running basic control programs
512 MB type 32 MB 480 MB (control application ≤ 10 MB) requires running Java applications such as InfoWell, or storing a large amount of historical data
(3) Network communication specifications
1. Ethernet (Control Network)
Standard compatibility: Following the IEEE802.3 standard, supporting dual redundancy configuration to ensure communication reliability.
Core purpose: To connect FCN/FCJ, PLC, display unit, VDS and other devices, and also for the development and maintenance of controllers (program download, parameter configuration).
Connection ability:
Remarks on the maximum number of connections for the connection target
VDS/FCN/FCJ OPC Server/FAST/TOOLS 4 units, total number of Class III devices not exceeding 4 units
FCN/FCJ controllers can link up to 15 devices of the same type with a single controller
32 third-party PLCs (such as FA-M3, MELSEC), each occupying 1 communication channel
2. Serial communication
Purpose: To connect display units, temperature controllers, power monitors, and other devices, supporting multiple serial communication protocols.
Hardware configuration:
Controller type serial port configuration remarks
FCJ 2 RS-232-C ports fixed configuration, non expandable
The FCN-100 CPU module comes with one RS-232-C port; Expandable serial communication module (2 ports per module, supporting RS-232-C or RS-422/RS-485) can install up to 8 expansion modules, and the CPU’s built-in serial port is not available when using dual redundant CPUs
(4) Control the upper limit of application capacity
Function Blocks (POUs): Supports up to 512, including:
Regulator control blocks (such as indicators, controllers, manual loaders): ≤ 128.
Other functional blocks (such as calculation block, switch instrument block, communication POU): ≤ 384.
Sequential program:
Ladder diagram: ≤ 180 kilosteps.
Sequence table: ≤ 128 (each table contains 32 condition rows+32 action rows).
Maximum configuration example:
I/O interface: 96 AI (analog input), 32 AO (analog output), 256 DI (digital input), 256 DO (digital output).
Control circuit: 32 PID circuits.
Sequence program: 128 sequence tables.
Control cycle: 1 second.
(5) Dual redundant CPU specifications (only supported by FCN-100)
Fault switching: After the main CPU fails, the backup CPU instantly takes over control permissions, and the switching process is undisturbed and does not affect system operation.
Balance operation: When adding or replacing CPU modules, the All program copy (APC) command needs to be executed to achieve data synchronization between two CPUs, and automatic execution is supported (only applicable to dual Style-3 NFCP100 CPU configurations); When the APC command runs, the first control cycle is extended by 1-2 seconds, and it returns to normal thereafter.
Operational restrictions:
Multi tasking cannot access the same global variable.
The CPU module’s built-in serial port is not available.
Unable to run Java application.
When configuring a non dual Style-3 NFCP100 CPU, the APC command needs to be manually executed. During execution, the control pauses, and the I/O module runs according to the Fallback option (such as maintaining output or outputting specified values).